Tutorials:Token Ecosystem: Difference between revisions
BeginnersGuide>Marin No edit summary |
m (1 revision imported) |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 18:13, 29 October 2025
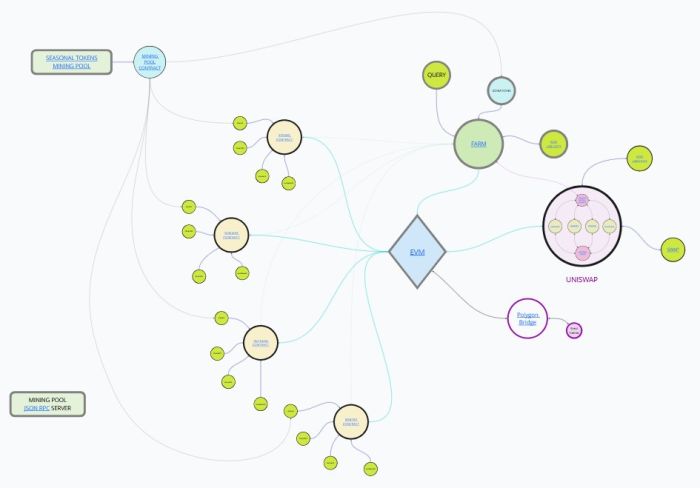
Seasonal Tokens Ecosystem
Lets have an overview of the Seasonal Tokens Ecosystem. View Clickable Links Image Here These are the elements involved in the system:
- Token Smart Contracts.
- Mining Pools.
- Decentralized Market (Uniswap).
- Farm Smart Contracts.
- Bridge connecting the Polygon and Ethereum Networks
The system is autonomous and self sufficient
It is important to notice that this token ecosystem works autonomously, and completely decentralized. All tasks that can be performed will be performed when there is an economic advantage in doing so.
For example:
- Mining will be done if you can sell the tokens and make profit. Otherwise mining will stop, this will lead to decrease in difficulty, and this will lead to cheaper mining, until mining is profitable again.
- Trading will be done when there is profit to make.
- Farming will happen if participants get money by doing so.
- The Polygon Bridge will be used if there are markets in Polygon to sell tokens.
- Tokens will move from one network to another if the price difference is enough to make profits.
Seasonal Tokens in Polygon
The above image shows the Ethereum part of the Seasonal Tokens ecosystem. There are other smart contracts associated but they are in the Polygon blockchain.
The Seasonal Tokens Ecosystem in Polygon looks the same as this one except for one very important thing:
The smart contracts in Polygon do not have the "Mint" function
The tokens are created in the Ethereum network, and some of them are sent over to the Polygon network using the Bridge Technology.
Polygon then creates "Wrapped" versions of the tokens.
The Polygon bridge "owns" the tokens, and gives to the users "wrapped" tokens at a one to one exchange rate.
Task:
Find the Uniswap V3: Liquidity Positions Manager. Use the Miro Board with clickable links to find it.
Hint: It starts with 0xc36...