Tutorials:Analyzing the Bitcoin Price History Chart: Difference between revisions
m (1 revision imported) |
m (Move page script moved page Tutorials:3eef to Tutorials:Analyzing the Bitcoin Price History Chart) |
(No difference)
| |
Latest revision as of 01:41, 4 November 2025
Quest: Analyzing the Bitcoin Price History Chart
In this exercise, we will use TradingView's tools to analyze data:
TradingView Bitcoin Price Chart
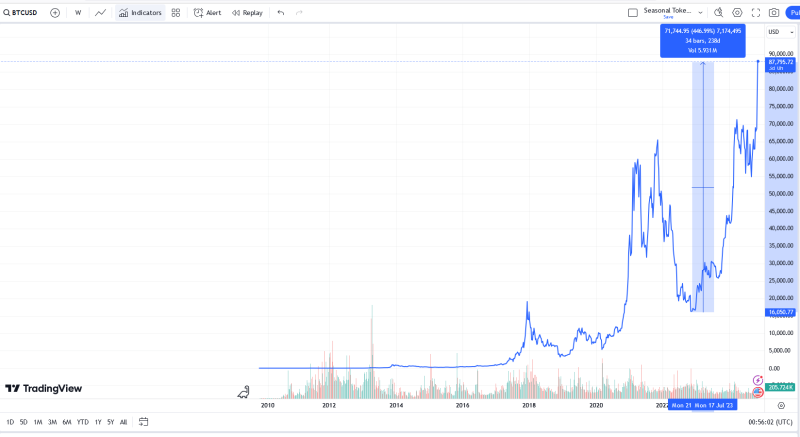
We will use the Ruler tool to measure the percent of growth from the latest bottom in the chart to the latest peak.
Steps:
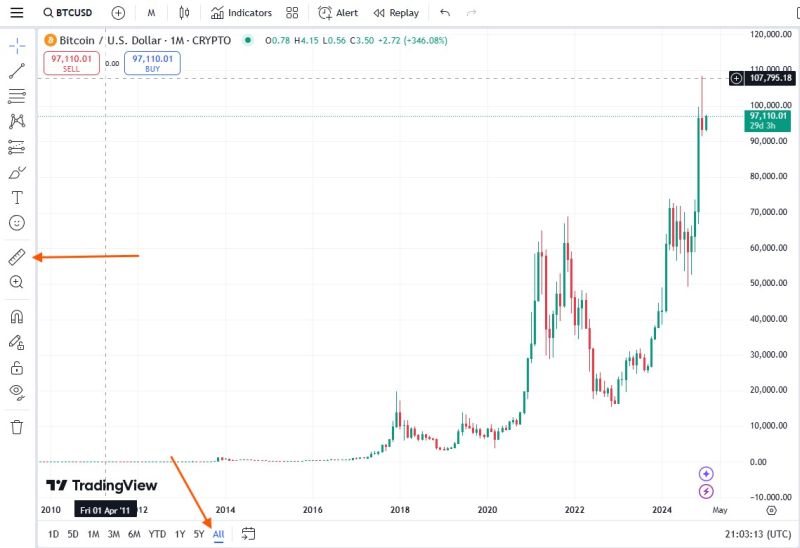
- Select "All" for the time range of the chart. (located in the bottom left)
- Use the Ruler Icon located on the left-hand side of the chart.
- Measure the height of the last Bitcoin price spike, starting from the bottom of the bear market at the end of 2022 / Beginning of 2023.
- Click and drag the mouse from the bottom of the chart to the peak, a rectangle will appear showing the increase in price, then the percentage of growth in parentheses.
Exercise
Notice the percentage of the price increase from the bottom of the last bear market to the present.
Task
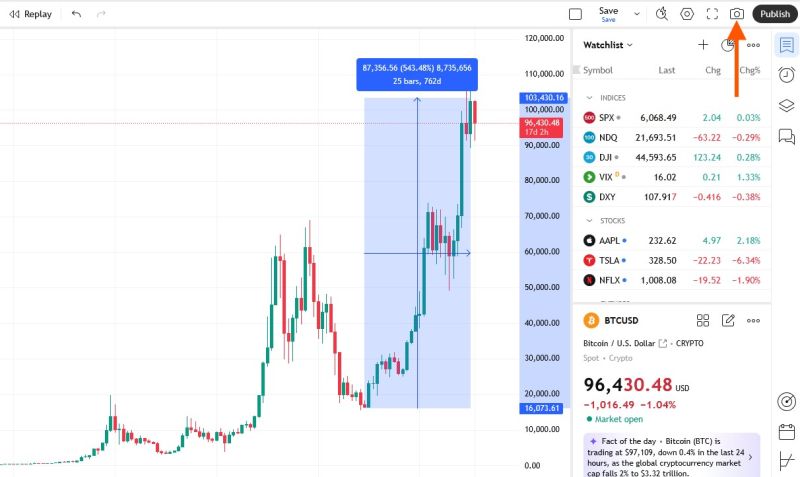
- Click on the Camera Icon, marked by the orange arrow in the image below.
- Select: Copy Link.
- Share the link to complete the quest.
Discussion
Proof of work mining connects Bitcoin to the real world economy:
Bitcoin is a digital asset produced by proof of work mining, a process that effectively converts energy into currency.
It is closer to a physical "commodity" like the products of mining or agriculture.
The Bitcoin network is self sustainable because nodes are rewarded with new Bitcoins created every 10 minutes on average, and with the tips included with transactions to be processed faster than others with less tips.
One of the most important features of Bitcoin to make it the ideal store of value is that there are only 21 million Bitcoins. It is impossible to create more. To keep this number fixed, the mining supply of Bitcoin is reduced by 50% every 210,000 blocks, or every 4 years on average (One block is produced every 10 minutes on average). This event is called "halving" of mining supply, or simply the halving.
Key Insight:
The halving of mining supply effectively duplicates the cost of production of Bitcoin overnight, this leaves many miners out of business. This forces miners to rise the price of Bitcoin to keep the mining profitability. In other words:
Bitcoin's price has an upward pressure because every four years the cost of production of Bitcoin doubles overnight.
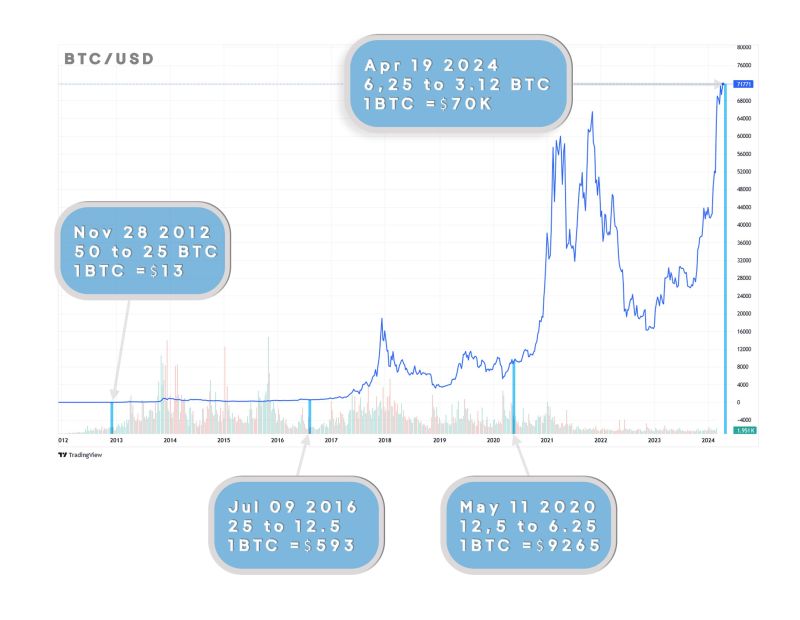
At the time of this writing Bitcoin's mining supply has been halved four times:
| Date | Previous Reward | New Reward | BTC Price USD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11/28/2012 | 50 | 25 | 13 |
| 07/09/2016 | 25 | 12.5 | 593 |
| 05/11/2020 | 12.5 | 6.25 | 9,265 |
| 04/19/2024 | 6.25 | 3.12 | 70,000 |
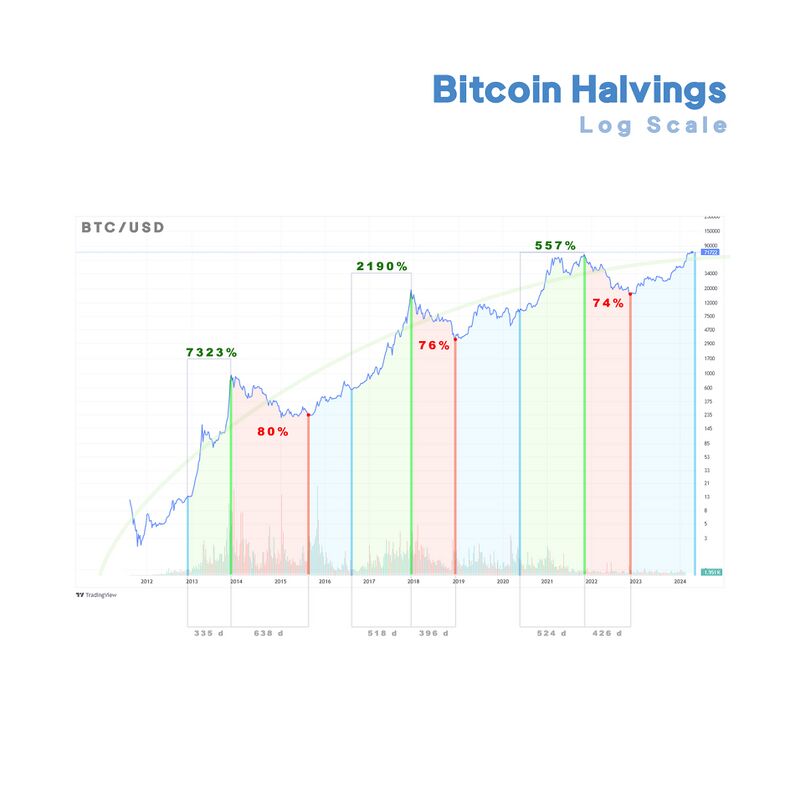
These dates are marked by blue lines in the following graph. Notice that the price variation has been so large that the price variations in the first years are almost invisible.
BTC Price Chart Logarithmic scale
Let's have a look at the same data but in the logarithmic scale. We have highlighted the relevant features for discussion:
The green area is the so called "Bull Run" it begins from the day of the halving to the local maximum in price. You can see that the first bull run saw a price increase of 7323%, the second bull run caused a price increase of 2190%, and the third a 557%.
After a bull run, Bitcoin price reaches a price bubble and this leads to a "Bear Market" (Marked in Red in the graph) where the price falls more than 70%
The blue area marks a period of recovery leading to the next Bitcoin halving.
This periodic behavior caused by the halving of mining supply is the most important observation in Crypto, by adopting a long term view investors can make money without excessive risk.
Trading short term price fluctuations is very difficult, and most traders lose their money doing that. It has become a well known proverb: Don't trade more than you are prepared to lose.