Tutorials:Layer II: Difference between revisions
m (1 revision imported) |
No edit summary |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Layer II Bridges and Wrapped Tokens= | In the tutorials we will be using the Polygon network only because of the very low fees. | ||
=Layer II Networks. Bridges and Wrapped Tokens= | |||
Layer II networks are solutions built on top of Layer I blockchains, like Ethereum, to improve scalability and reduce transaction costs. They help handle a large number of transactions off-chain while still relying on the main blockchain for security and finality. | Layer II networks are solutions built on top of Layer I blockchains, like Ethereum, to improve scalability and reduce transaction costs. They help handle a large number of transactions off-chain while still relying on the main blockchain for security and finality. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 8: | ||
The '''Polygon Network''' is a popular Layer II solution for Ethereum. It offers faster transactions and significantly lower fees, making it ideal for swapping and trading tokens. By using Polygon, users can enjoy the benefits of Ethereum's ecosystem—like smart contracts and dApps—without the high gas fees typically associated with the Ethereum mainnet. | The '''Polygon Network''' is a popular Layer II solution for Ethereum. It offers faster transactions and significantly lower fees, making it ideal for swapping and trading tokens. By using Polygon, users can enjoy the benefits of Ethereum's ecosystem—like smart contracts and dApps—without the high gas fees typically associated with the Ethereum mainnet. | ||
= | =Polygon Bridge and Wrapped Tokens= | ||
The '''Polygon Bridge''' is a tool that enables the transfer of tokens between the Ethereum and Polygon networks. Since these two blockchains operate independently, tokens cannot be directly moved between them. Instead, the tokens are '''wrapped''' when transferred across the bridge. Wrapped tokens are representations of assets from one blockchain on another, maintained at a '''1:1 ratio'''. | |||
If you send tokens from one network address to an address in another network you will loose them. | |||
The only way to "move" tokens from one blockchain to another is using the '''Bridge''' technology. | |||
'''Example:''' Seasonal Tokens are produced on the Ethereum network but are traded on the Polygon network due to its lower transaction fees. | |||
To facilitate this, users send their tokens through the Polygon Bridge. The bridge locks the original tokens on Ethereum and issues wrapped equivalents on Polygon, ensuring that the total supply remains consistent across both networks. | |||
'' | ''This mechanism allows Seasonal Tokens to be mined on Ethereum and traded efficiently on Polygon.'' | ||
=Bridge Tokens from one Network to Another= | |||
We can "bridge" tokens from one network to another using Metamask's built in function SWAP. Or visiting directly the bridge page. | |||
For example: https://portal.polygon.technology/bridge | |||
Suppose we want to send Winter tokens from the Ethereum to the Polygon network. In Metamask click in the "SWAP" tab to get: | |||
[[File: | [[File:Bridge 1.png|400px]] | ||
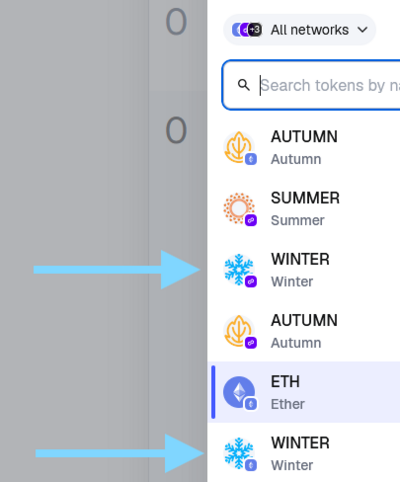
We will choose Winter in Ethereum as the source, and Winter in Polygon as the destination. | |||
[[File:Bridge 2.png|400px]] | |||
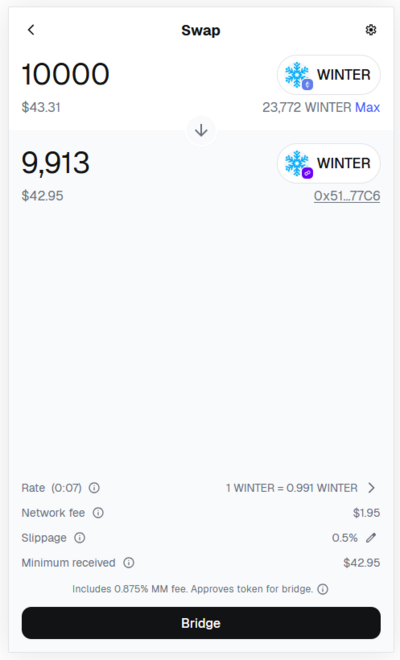
This swap will in fact use the Polygon Bridge in order to "send" the tokens from one network to another. | |||
[[File:Bridge 3.png|400px]] | |||
=Arbitrage= | |||
Since the token's prices are determined by the liquidity pools in the Ethereum and Polygon networks. Their prices are not the same, and also a small fee will be charged for the swap from one network to the other. | |||
Sometimes the price difference in two networks can present an economic incentive to send tokens from one network to another. A situation called "Arbitrage". | |||
Latest revision as of 03:00, 9 January 2026
In the tutorials we will be using the Polygon network only because of the very low fees.
Layer II Networks. Bridges and Wrapped Tokens
Layer II networks are solutions built on top of Layer I blockchains, like Ethereum, to improve scalability and reduce transaction costs. They help handle a large number of transactions off-chain while still relying on the main blockchain for security and finality.
The Polygon Network is a popular Layer II solution for Ethereum. It offers faster transactions and significantly lower fees, making it ideal for swapping and trading tokens. By using Polygon, users can enjoy the benefits of Ethereum's ecosystem—like smart contracts and dApps—without the high gas fees typically associated with the Ethereum mainnet.
Polygon Bridge and Wrapped Tokens
The Polygon Bridge is a tool that enables the transfer of tokens between the Ethereum and Polygon networks. Since these two blockchains operate independently, tokens cannot be directly moved between them. Instead, the tokens are wrapped when transferred across the bridge. Wrapped tokens are representations of assets from one blockchain on another, maintained at a 1:1 ratio.
If you send tokens from one network address to an address in another network you will loose them.
The only way to "move" tokens from one blockchain to another is using the Bridge technology.
Example: Seasonal Tokens are produced on the Ethereum network but are traded on the Polygon network due to its lower transaction fees.
To facilitate this, users send their tokens through the Polygon Bridge. The bridge locks the original tokens on Ethereum and issues wrapped equivalents on Polygon, ensuring that the total supply remains consistent across both networks.
This mechanism allows Seasonal Tokens to be mined on Ethereum and traded efficiently on Polygon.
Bridge Tokens from one Network to Another
We can "bridge" tokens from one network to another using Metamask's built in function SWAP. Or visiting directly the bridge page. For example: https://portal.polygon.technology/bridge
Suppose we want to send Winter tokens from the Ethereum to the Polygon network. In Metamask click in the "SWAP" tab to get:
We will choose Winter in Ethereum as the source, and Winter in Polygon as the destination.
This swap will in fact use the Polygon Bridge in order to "send" the tokens from one network to another.
Arbitrage
Since the token's prices are determined by the liquidity pools in the Ethereum and Polygon networks. Their prices are not the same, and also a small fee will be charged for the swap from one network to the other.
Sometimes the price difference in two networks can present an economic incentive to send tokens from one network to another. A situation called "Arbitrage".