Tutorials:Private Keys and Public Address: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Private Keys and Public Address= | =Private Keys and Public Address= | ||
In Ethereum-style networks, private keys and public addresses are two sides of the same cryptographic identity. | In Ethereum-style networks, ``private keys`` and public addresses are two sides of the same cryptographic identity. | ||
A private key is a long, randomly generated number that only you should know. It is the secret that gives you control over your funds. When you send a transaction, your wallet uses the private key to create a digital signature that proves you authorized the action—without ever revealing the key itself. Anyone who gets access to your private key can fully control your assets. | A private key is a long, randomly generated number that only you should know. It is the secret that gives you control over your funds. When you send a transaction, your wallet uses the private key to create a digital signature that proves you authorized the action—without ever revealing the key itself. Anyone who gets access to your private key can fully control your assets. | ||
Revision as of 01:37, 9 January 2026
Private Keys and Public Address
In Ethereum-style networks, ``private keys`` and public addresses are two sides of the same cryptographic identity.
A private key is a long, randomly generated number that only you should know. It is the secret that gives you control over your funds. When you send a transaction, your wallet uses the private key to create a digital signature that proves you authorized the action—without ever revealing the key itself. Anyone who gets access to your private key can fully control your assets.
A public address is derived mathematically from the private key. It’s safe to share and acts like an account number. Others can send ETH or tokens to this address, and anyone can view its balances and transaction history on the blockchain, but no one can spend from it without the corresponding private key.
In short:
Private key → proves ownership and signs transactions (keep it secret)
Public address → receives funds and is visible on-chain (safe to share)
Your wallet simply manages this key pair for you, making the cryptography invisible while you interact with the network.
In the next sections we will find in Metamask the private key of your Account1, the public address (often thought as the account "number"), and the recovery phrase. The private key can be used to import an account to other wallet, however, the new wallet cannot generate an imported account from the recovery phrase.
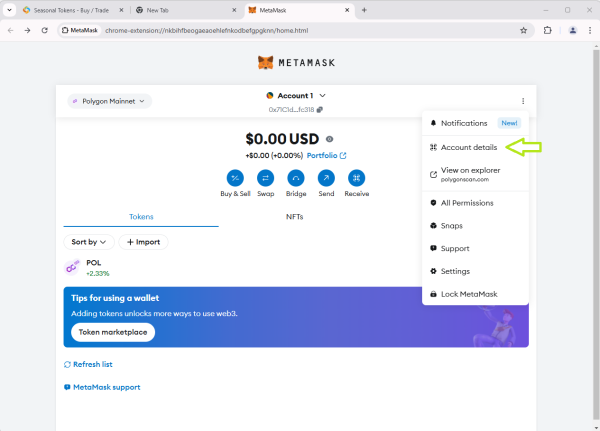
In Metamask see under Account 1, that is the public address.
In Ethereum and compatible blockchains public addresses start with the prefix 0x
- Click on the 3 dots besides your account name, and select account details.
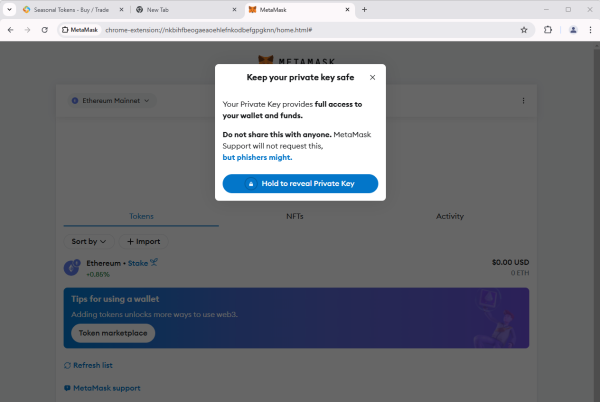
- Click on show private key.
Task:
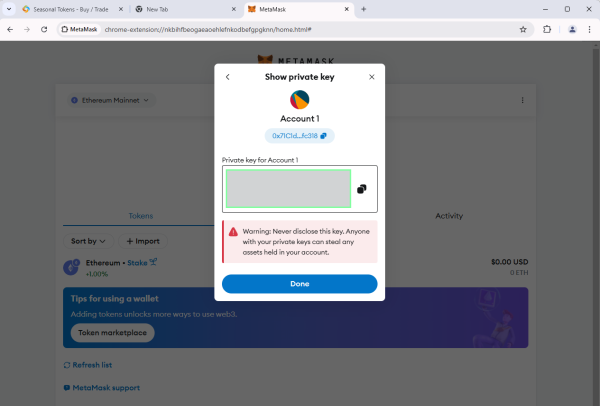
Look at the Private Key of your account, how many characters it has? 64, 32, 16
Exercise
With a Private Key you can import the associated account from any wallet on any device. whoever has the private key, controls the funds associated with that address.